"Kirk Critic Watchdog Site Vanishes After Raising Thousands, Leaving Donors Outraged and Questions Over Funds"
MAGA Site Exposing Charlie Kirk's Critics Disappears
"Expose Charlie’s Murderers" Site Disappears After Fundraising
Major Shock: The MAGA movement's circles were rocked by the disappearance of a website that vowed to build a massive database to expose the identities of Charlie Kirk's critics, after collecting tens of thousands of dollars in cryptocurrency. The site, known as "Expose Charlie’s Murderers," launched hours after the September shooting targeting the 31-year-old right-wing influencer, promising to create a comprehensive, searchable registry of individuals' names and workplaces to assist in what they called "the largest firing in history" against his detractors.
According to a report published by "Drop Site" about the now-unavailable project, the site collected over $30,000 between September 12 and 14 across six cryptocurrency wallets. Afterwards, the site repeatedly disappeared then reappeared under the name "Charlie Kirk Data Foundation" before vanishing completely again. The project organizers, calling themselves "Anon Palantir," published 41 entries including screenshots of posts by people who mocked or criticized Kirk, before the project abruptly halted.
Repercussions of the Campaign on Targets and the Fate of the Funds
Widespread Outrage: This incident sparked widespread outrage among donors, with one expressing a desire to reclaim their donation, while others described the organizing group as "liars" and "fraudsters." Meanwhile, individuals targeted by this misleading campaign faced a barrage of threats and harassment at their workplaces. For example, in Oregon, a local school board chair was forced to resign on October 7, after having written that she "would not mourn" Kirk. She later reported to "Drop News" that she had received "frightening and horrific" harassment.
It is worth noting that Charlie Kirk, a prominent and well-known influencer in the MAGA movement, was shot and killed on the campus of Utah Valley University on September 10. This incident sparked a wave of grief in conservative circles and led to the spread of far-right conspiracy theories, as well as posts aimed at escalating anger. The website that targeted Kirk's critics exploited this charged atmosphere, boasting of receiving "63,648 requests," despite publishing only a few entries. According to "Drop Site," the site's domains—registered via Namecheap then Epik—were withdrawn or dropped due to the use of falsified registration data and threats of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
In a related context, a third site, registered under the name "Franklin Hurd" in an office building in Spokane, a building used by multiple companies, also disappeared. "Drop Site" received no response from the project organizers or listed contacts regarding the fate of the collected funds. In the aftermath of the incident, officials appealed to the public for calm as the investigation into the September 10 shooting progressed, and warned against launching retaliatory "doxing" campaigns targeting Kirk's critics. "The Daily Beast" attempted to contact the project's operators and registrars for comment on these developments.
About Charlie Kirk and the MAGA Movement
Charlie Kirk was a conservative American media personality, a prominent political activist, and the founder of the non-profit organization "Turning Point USA." He is known for his support of the "Make America Great Again" (MAGA) movement, which represents a slogan and political movement associated with former US President Donald Trump, focusing on promoting conservative values and nationalist policies.
What is a Knowledge Graph?

A Knowledge Graph is a structurally organized database that stores information in a way that describes relationships between different entities. It functions as a semantic network connecting concepts, entities, and facts, enabling a deeper understanding of the context and meaning behind the data. Its goal is to enable intelligent systems to understand the world in a human-like manner, by building a network of interconnected knowledge.
Essential Components of a Knowledge Graph

A Knowledge Graph fundamentally consists of three interconnected elements:
- Entities: These are the things or concepts being discussed, such as people, places, organizations, or ideas.
- Relationships: The links that define how entities are connected to each other. For example, "X is the author of Y" or "Z is located in city A."
- Attributes: Characteristics that describe entities, such as a person's birth date or a city's population.
Benefits of Using Knowledge Graphs

Knowledge Graphs offer a wide range of benefits, most notably:
- Enhanced Search and Understanding: They help search engines and intelligent systems better understand user queries and deliver more accurate and relevant results.
- Data Enrichment: They allow different datasets to be linked together, revealing new insights and hidden relationships.
- Support for Artificial Intelligence: They provide a strong foundation for AI and machine learning applications, such as recommendation systems and virtual assistants.
- Improved User Experience: They enable the delivery of organized and easily understandable information to users, enhancing their interaction with content.
Use Cases for Knowledge Graphs
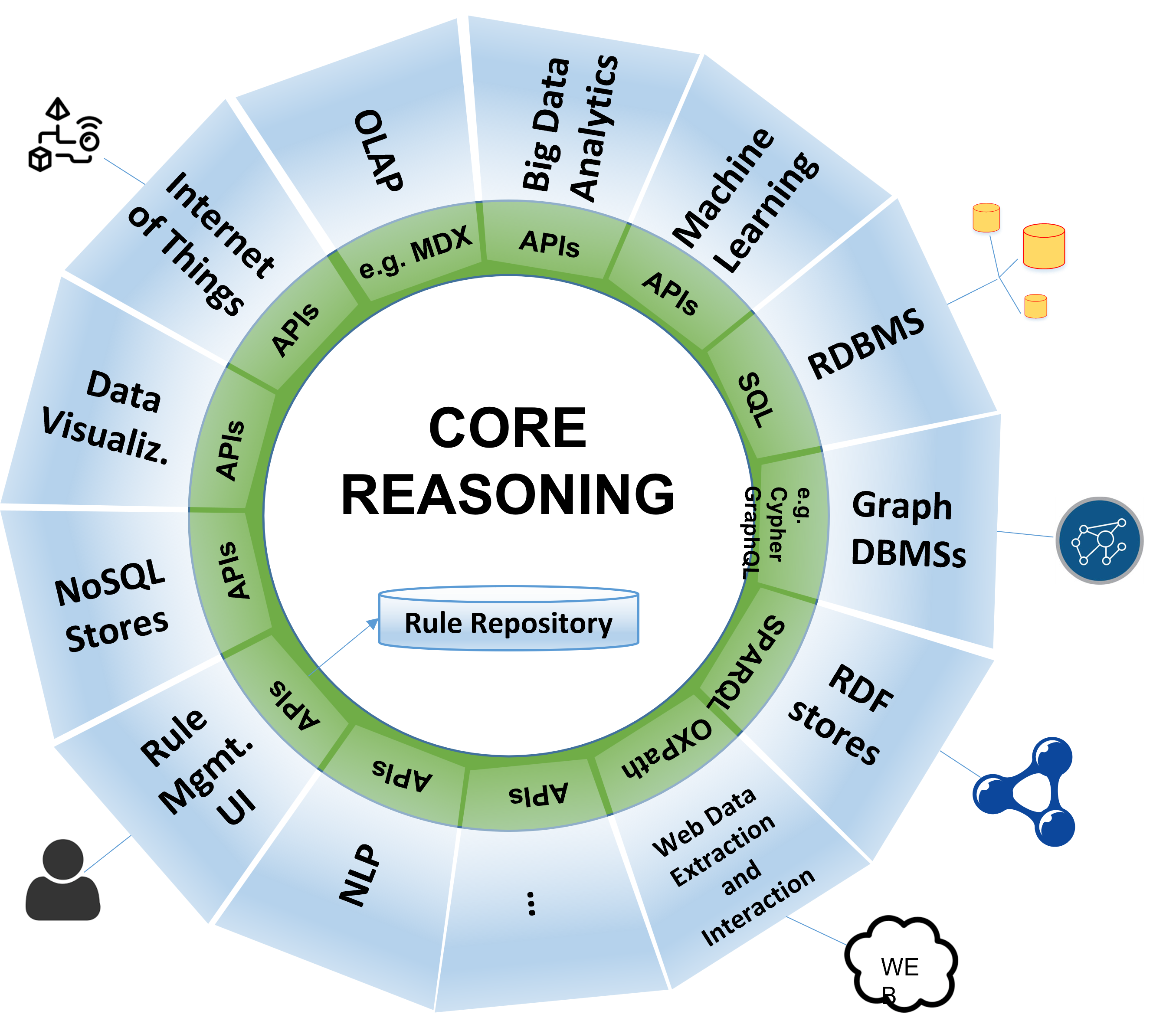
Knowledge Graphs are used in a wide range of fields and applications, including:
- Search Engines: To improve understanding of search queries and provide information-rich results (e.g., knowledge panels in Google results).
- Healthcare: To connect patient data, medications, diseases, and treatments to improve diagnosis and care.
- E-commerce: To provide accurate product recommendations based on user preferences and product relationships.
- Financial Services: To detect fraud and analyze risks by linking transactions and entities.
- Intelligence and Data Analysis: To identify relationships and patterns in large and complex datasets.
Building a Knowledge Graph

Building a Knowledge Graph typically involves several key stages:
- Data Extraction: Gathering information from diverse sources such as unstructured texts (documents, web pages), databases, and structured data.
- Entity and Relationship Extraction: Identifying core entities (e.g., people, places) and the relationships between them using natural language processing and machine learning techniques.
- Data Harmonization: Merging identical entities from different sources and removing duplicates to ensure consistency.
- Graph Storage: Using specialized graph databases (e.g., Neo4j, JanusGraph) to efficiently store entities and relationships.
- Inference and Expansion: Using logic rules and machine learning to infer new information and automatically expand the graph.
Challenges in Building Knowledge Graphs

Building Knowledge Graphs faces several key challenges:
- Data Quality: Collecting and harmonizing data from multiple and inconsistent sources can be complex.
- Scalability: Managing enormous knowledge graphs containing billions of entities and relationships requires robust infrastructure.
- Information Extraction: Accurately extracting entities and relationships from unstructured texts requires advanced techniques and intensive processing.
- Maintenance and Updates: Continuously keeping the knowledge graph updated and evolving as information changes.
Future Trends in Knowledge Graphs

Knowledge Graphs are evolving in several future directions, including:
- Open Knowledge Graphs: Increased collaboration and data sharing to create large-scale public knowledge graphs.
- AI-Powered Knowledge Graphs: Deeper integration with deep learning technologies to enhance inference and automated knowledge discovery.
- Temporal and Spatial Knowledge Graphs: Developing the ability to represent and track changes in knowledge across time and space.
- Personalized Knowledge Graphs: Creating customized graphs for users to provide more individualized experiences.
