Tylenol, Autism, and COVID-19: Health Minister's Statements and a New Study
Controversy Surrounds Tylenol (Paracetamol) and its Link to Autism
The Paracetamol and Autism Debate: Statements and Warnings
U.S. Health Secretary, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., stated that there is not enough conclusive data to confirm that Tylenol (Paracetamol) drug causes autism. Kennedy clarified that the causal link between paracetamol use during pregnancy and the perinatal periods "is not sufficient to definitively say it causes autism, but it is very suggestive." The Secretary advised a cautious approach when using the drug, pointing to the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before taking any medication during pregnancy. These statements come a month after previous warnings from President Donald Trump, who is not a doctor, to pregnant women against taking this medication without clear scientific evidence at that time. Trump's unsubstantiated claims then affected the shares of Kenvue, which spun off from Johnson & Johnson in 2023. Many doctors and Kenvue have repeatedly defended the pain reliever, asserting no confirmed scientific link between it and autism, and warned that such suggestions could endanger maternal health by avoiding a safe and essential drug for pain and fever relief. The company also urged the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to reject any claims for an autism warning on the Tylenol label.
Scientific Evidence: Studies Supporting a Potential Link
The debate over the use of Paracetamol (Tylenol) during pregnancy and its relationship to neurodevelopmental disorders has seen numerous studies. Multiple studies have indicated a link between maternal exposure to paracetamol during pregnancy and an increased risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children. For example, a study published in Environmental Health and a systematic review in PubMed found that prenatal paracetamol exposure was associated with an increased risk of ADHD (odds ratio: 1.26) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (odds ratio: 1.19). A study from Mount Sinai also stated that prenatal paracetamol exposure may increase the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism and ADHD (Environmental Health, 2025), (PubMed Central), (Mount Sinai, 2025). This evidence has prompted the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to initiate a process to change the paracetamol label to reflect these potential associations (FDA, 2025).
Opposing Views and Recommendations from Health Organizations
However, it is important to note that these studies are often observational and do not establish a direct causal relationship. Other studies, particularly those using sibling analysis to control for confounding family factors, found no evidence of an increased risk of autism or ADHD with paracetamol use during pregnancy (Johns Hopkins, 2025), (PubMed, 2024), (Figo). Major health organizations, such as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the UK National Health Service (NHS), still consider paracetamol the first and safe choice for pain relief and fever reduction during pregnancy when used correctly (ACOG, 2025), (Cleveland Clinic, 2025), (The Guardian, 2025). Doctors always advise consulting a healthcare provider before taking any medication during pregnancy.
Impact of COVID-19 and Artificial Intelligence in Research
This debate coincides with another recent study indicating that children born to mothers who contracted COVID-19 during pregnancy faced a higher risk of autism, in addition to other neurological differences such as delayed speech and motor development. This study, published in "Obstetrics and Gynecology," included over 18,100 births in Massachusetts, USA. These findings highlight the importance of continued rigorous scientific research to understand the complex factors that may affect child development. Artificial intelligence can play an increasingly important role in analyzing these large datasets to help uncover new patterns and relationships.
Understanding Knowledge Graphs
What is a Knowledge Graph?
A Knowledge Graph is a structured database based on the concept of graphs to represent knowledge. It connects various entities (such as people, places, events, concepts) and the relationships between them, allowing for context understanding and semantic search. Knowledge graphs are used to store data in a way that facilitates human and machine understanding, offering deep insights by showing how pieces of information are related to each other. They can be defined as a network of interconnected entities and relationships that describe a specific domain of knowledge or a world of facts.

Key Components of a Knowledge Graph
A Knowledge Graph primarily consists of three elements:
- Entities: These are the nodes in the graph and represent real-world objects or concepts (e.g., person, place, organization, event, idea).
- Relations/Edges: These are the links between entities that describe how entities are connected to each other (e.g., "works for," "author of," "located in").
- Attributes/Properties: These are properties that describe entities (e.g., name, date of birth, location).
These components allow for the construction of a semantic network rich in information that can be efficiently explored and analyzed.

Benefits of Using Knowledge Graphs
Knowledge Graphs offer several benefits that enhance data understanding and usage:
- Improved Search and Information Discovery: They enable semantic search that understands the context of queries, leading to more accurate and relevant results.
- Data Integration: They connect data from multiple, disparate sources into a unified structure, making it easier to access and analyze.
- Support for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: They provide rich context for intelligent models, improving their ability to understand natural language, make decisions, and provide recommendations.
- Knowledge Management: They help organizations systematically organize their internal and external knowledge, enhancing collaboration and information exchange.
- Discovery of Hidden Insights: They reveal relationships and patterns that may not be apparent in traditional databases, leading to valuable insights.
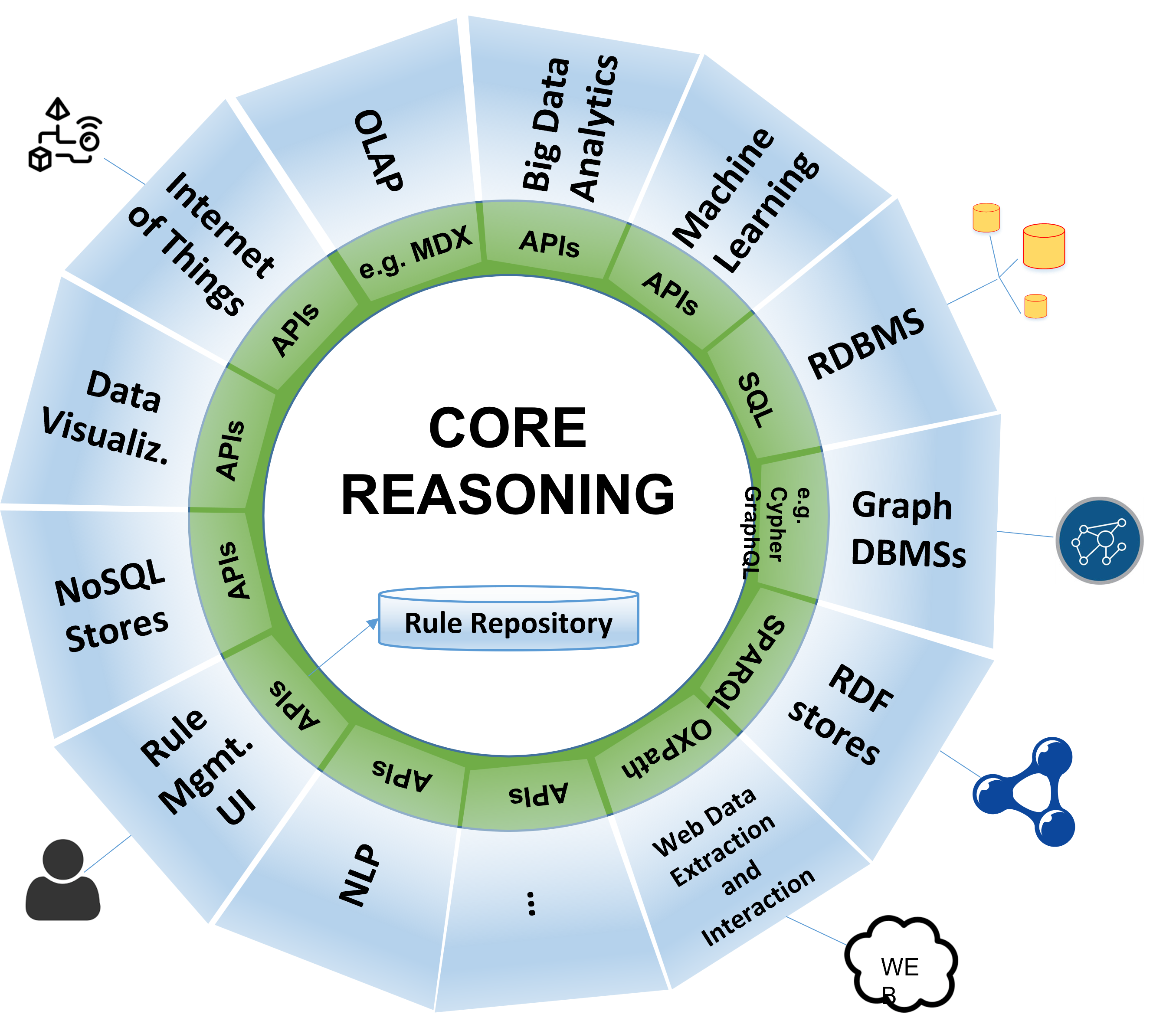
Use Cases of Knowledge Graphs
Knowledge Graphs are used in a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Search Engines (e.g., Google Knowledge Graph): To improve understanding of user queries and provide direct, rich information.
- E-commerce: To enhance product recommendations, analyze customer behavior, and organize complex product catalogs.
- Healthcare and Drug Discovery: To link information about diseases, drugs, genes, and proteins to accelerate research and development.
- Financial Services: For fraud detection, risk analysis, and understanding relationships between financial entities.
- Intelligence and Data Analysis: To connect disparate information from various sources to uncover patterns and provide security and intelligence insights.
- Recommendation Systems: In streaming services, social media, and e-commerce to provide personalized content to users.

Building a Knowledge Graph
Building a Knowledge Graph involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: Data is collected from various sources such as relational databases, unstructured texts, APIs, and web pages.
- Entity and Relation Extraction: Important entities and concepts, as well as the relationships between them, are identified, often using Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning techniques.
- Schema Definition: The graph's structure is defined, including types of entities, relationships, and attributes, often using specific Ontologies or Schemas.
- Entity Linking/Resolution: Extracted entities are matched with existing entities in the graph to avoid duplication and create unified links.
- Knowledge Graph Enrichment: Adding new information or inferring implicit relationships based on existing data to increase the richness of the graph.
- Storage and Querying: The graph is stored in a Graph Database and specialized query languages (e.g., SPARQL) are used to access information.

Challenges in Building Knowledge Graphs
Despite their benefits, the process of building Knowledge Graphs faces several challenges:
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data from various sources can be extremely complex.
- Handling Unstructured Data: Extracting entities and relationships from texts, images, and videos requires advanced techniques and intensive processing.
- Scalability: As data volume grows, the complexity of managing, storing, and querying knowledge graphs increases.
- Schema and Ontology Evolution: Keeping the schema and ontology updated to accommodate changing and evolving data requires continuous effort.
- Entity Resolution: Accurately determining whether different entities refer to the same thing (e.g., "New York" and "New York City") is a significant challenge.
- Knowledge Graph Maintenance: Requires continuous updating of knowledge graphs to reflect new information and changing relationships.

Future Trends in Knowledge Graphs
Knowledge Graphs are undergoing continuous developments that promise to expand their scope and effectiveness:
- Dynamic Knowledge Graphs: The ability to update and adapt knowledge graphs in real-time with new data streams.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Using knowledge graphs to make AI model decisions more transparent and understandable.
- Integration of Knowledge Graphs with Large Language Models (LLMs): Combining the power of knowledge graphs in providing structured context with the ability of large language models to understand and generate text.
- Cybersecurity: Increasing applications in threat detection and analysis by linking security entities and their relationships.
- Open Knowledge Graphs: Increased collaboration in building open-source and shared knowledge graphs to support research and innovation.
- Personal Knowledge Graphs: Developing personalized knowledge graphs for individuals to organize their personal information and preferences.

